Press Releases
* Please note that the news release contains the content at the time of the announcement and may differ from the latest information.
Notice of patent application regarding immune balance regulation function by continuous intake of paramylon
-It was suggested that it may be possible to maintain the immune balance and prevent the onset of the disease-
Euglena Co., Ltd.
Euglena Co., Ltd. (Headquarters: Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, President: Mitsuru Izumo) has announced that it has applied for a patent on April 8, 2014 regarding the immune balance adjustment function by continuous ingestion of paramylon, a unique component of the Euglena To do.
It is said that the risk of contracting various diseases can be reduced by balancing the substances related to immunity with each other. This time, as an empirical study, we investigated the effect on immune function when paramylon, a polysaccharide peculiar to Euglena
As a result, it was shown that continuous intake of paramylon may affect the pattern of lymphocyte cytokine * 1 production and regulate the immune balance. Specifically, paramylon may adjust the balance between cell-mediated immunity and humoral immunity * 2 and prevent the development of diseases caused by bias toward either. Following this verification, we have applied for a patent this time.
These results are consistent with the report * 3 on improvement of atopic dermatitis sign of paramilon published in Laboratory Animal Science in 2010, and the immune system shown in this data is shown. It is considered that the regulation of atopic dermatitis is one of the mechanism of action for improving the sign of atopic dermatitis.
In the future, we will further research the immune function of paramylon, aiming to utilize it in the medical field and improve the added value of Euglena In addition, details of the data will be reported at future academic conferences and treatises as appropriate.
The details are as follows.
* 1 Cytokine: A substance that communicates between cells and proliferates, differentiates, and expresses functions.
* 2 Cell-mediated immunity and humoral immunity: Cell-mediated immunity is an immune response that is mainly caused by phagocytic cells, and humoral immunity is an immune response that is mainly caused by antibodies. It is reported that the predominance of cell-mediated immunity may increase the possibility of improving the initial defense against infection, but the excess may cause autoimmune diseases that attack one's own cells. When humoral immunity becomes dominant, the ability to produce antibodies against foreign substances increases, but when it becomes excessive, it also produces antibodies against foreign substances that are not harmful to the body, increasing the possibility of inducing an allergic reaction. Immunity maintains an appropriate situation by maintaining a mutual balance between cell-mediated immunity and humoral immunity.
* 3 J Vet Med Sci. 2010 Jun; 72 (6): 755-63. Epub 2010 Feb 16.
About the immune balance regulation function by continuous intake of paramylon
■ Research content and results
○ We asked 10 people to take paramylon 1 g / day continuously for 8 weeks, and collected blood before and 8 weeks after ingestion.
○ When an immunity measurement test was performed using the collected blood, an increase in "cytokines of the cell-mediated immune system (IFN-γ)" and "cytokines of the humoral immune system (IL-)" were found in the lymphocytes in the blood. 4) ”decreased.
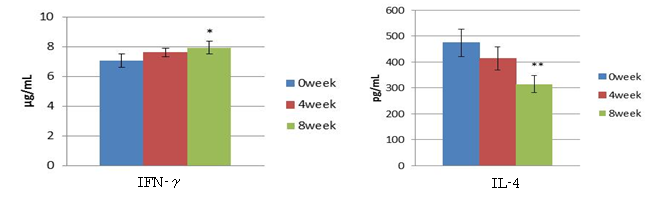 (* P <0.05, ** p <0.01, vs 0week)
(* P <0.05, ** p <0.01, vs 0week)
■ Consideration
It has been suggested that continuous intake of paramylon may regulate the balance between cell-mediated immunity and humoral immunity and prevent the development of diseases caused by bias toward either one.
-Contact for inquiries from the press-
Euglena Co., Ltd. Public Relations and IR Division
